[ad_1]
Credit lines are a lucrative product. U.S. consumers alone pay $120 billion in credit card interest and fees every year, according to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. Given the revenue opportunity, it’s no surprise that there’s enduring interest from both startups and established companies in delivering credit-based products. But challenges stand in the way, including — but not limited to — complying with local laws and regulations and modeling credit risk.
Enter Noble, a putative solution in the form of a platform that allows businesses to build credit-based products like credit cards and buy now, pay later services with no-code tools. Founded by WeWork veterans, Noble allows clients to connect data sources to create custom credit offerings, providing a rules-based engine to edit and launch credit models.
Noble today emerged from stealth and announced the close of a $15 million Series A round led by Insight Partners with participation from Cross River Digital Ventures, Plug & Play Ventures, Y Combinator, Flexport Fund, TLV Partners, Operator Partners, Verissimo Ventures, Interplay Ventures and the George Kaiser Family Foundation. The new cash brings the company’s total raised to $18 million, which CEO Tomer Biger tells TechCrunch will go toward opening a new office and expanding Noble’s portfolio to support additional use cases.

Connecting data sources in Noble’s admin dashboard. Image Credits: Noble
Biger and Noble’s CTO, Moran Mishan, worked together at WeWork on building underwriting infrastructure to help screen and assess the creditworthiness of tenants. Prior to WeWork, Biger was the product manager responsible for business-to-business (B2B) lender Behalf’s underwriting infrastructure, while Mishan was a software engineer at Woo.io, a job candidate sourcing platform.
“From these firsthand experiences, [we] saw how complicated it is for companies to build underwriting infrastructure and launch new credit-based products, Noble aims to change that,” Biger told TechCrunch in an email interview. “[We allow] companies to launch additional products that their end-customers want — access to credit.”
With Noble, companies can access credit bureaus, banks and income verification providers in deciding to which customers to extend credit lines (e.g. loans and cash advances). The platform’s interface lets businesses deploy workflows that automatically approve, decline or flag users for manual reviews, while on the backend customizing the experience to match a brand and auditing underwriting data from a single view.
“This increases lifetime value, boosts customer retention and ultimately can be an entirely new revenue source for companies,” Biger asserted. “Noble empowers … companies to do this quickly and efficiently without expending much internal engineering or product resources.”
Daniel Aronovitz, principal at Insight Partners, sees Noble’s primary customers as fintechs, software-as-a-service companies with financial offerings and B2B marketplaces and wholesalers. It’s early days, but he claims that the company already has “tens” of clients including major fintechs, with “millions of dollars” of loans originated through the Noble platform.
“With its strong product offerings and impressive founding team, Noble has already acquired B2B and business-to-consumer customers across use cases,” Aronovitz said in an emailed statement. “Noble has created a platform for credit underwriting infrastructure as a service, enabling any company to build proprietary credit products in-house.”
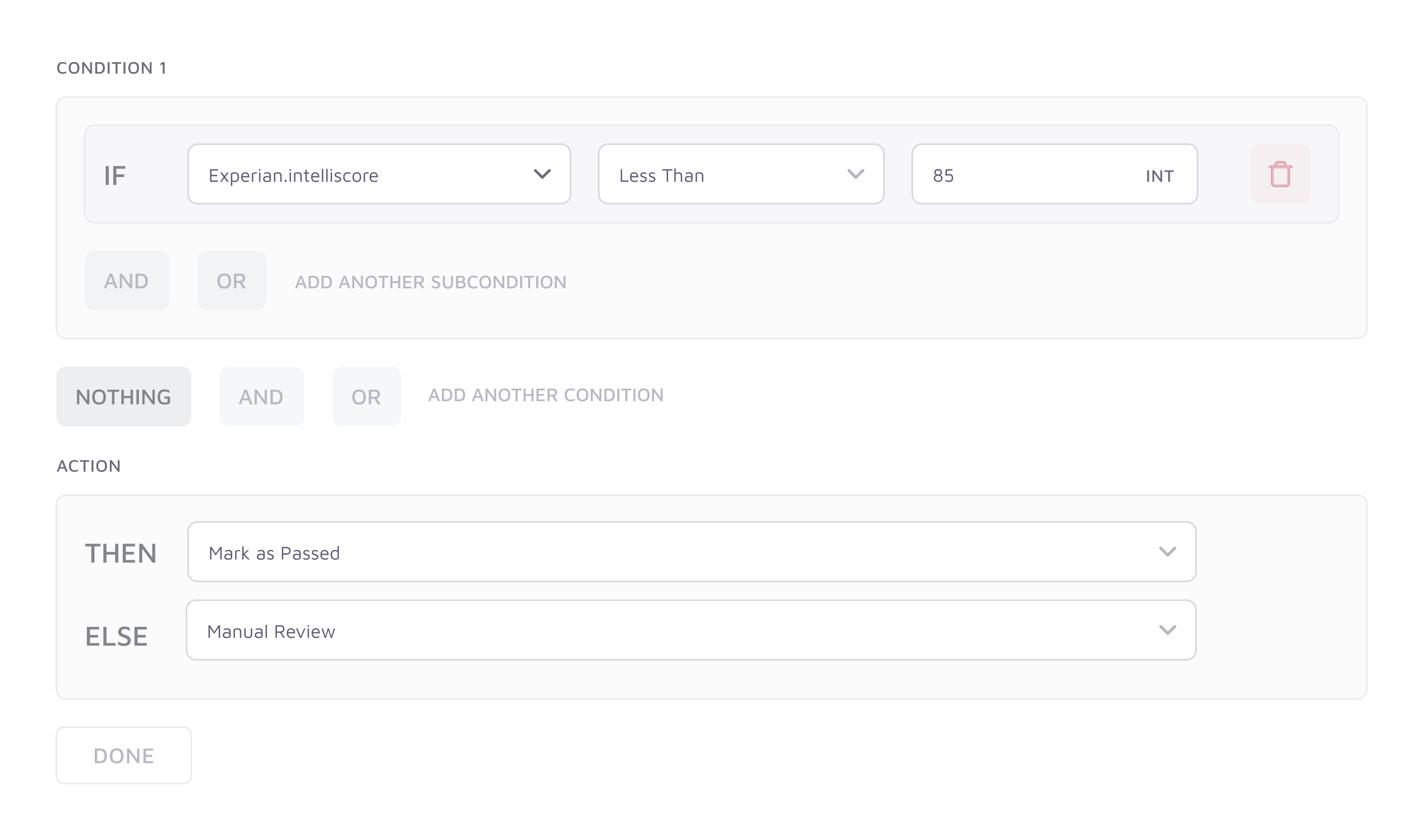
Conditional logic in Noble’s credit decisioning engine. Image Credits: Noble
But Noble isn’t unique in providing credit infrastructure. Fintech startup Alloy, which last year raised $100 million at a $1.35 billion valuation, recently expanded into automated credit underwriting. Stilt raised $114 million in March to expand its credit offerings. There are also firms like Finally, which focus on credit products for small- and medium-sized businesses.
For his part, Biger believes the market is robust enough that Noble isn’t at risk of getting crowded out. He’s not necessarily wrong — credit originated at the point of sale in the U.S. is projected to grow from about 7% of unsecured lending balances (i.e. without collateral) in 2019 to about 13% to 15% of balances by 2023, according to a McKinsey report. By 2023, the report projects that “pay in four” players — i.e. vendors like Klarna and Afterpay — will originate about $90 billion annually and generate around $4 billion to $6 billion in revenues.
Of course, credit products don’t guarantee profits — the buy now, pay later sector in particular has suffered steep losses and slashed valuations as of late. But Noble’s small-but-growing customer base proves that some companies, at least, are buying the sales pitch — and perhaps seeing some success.
“There are simply too many challenges that companies face when looking to build credit products including compliance, debt funding and underwriting,” Biger said. “Noble’s mission is to remove these barriers and enable the inevitable movement of lending experiences from offline to online in the same way that payment processing platforms built the new payment rails that enabled the explosive growth in online payments witnessed over the past decade.”
[ad_2]
Source link

